The Boycott, Divestment, Sanctions (BDS) movement is a global initiative led by Palestinians advocating for freedom, justice, and equality. The core principle underlying BDS is the belief that Palestinians should enjoy the same fundamental rights as any other people worldwide. The movement emerged in response to Israel’s occupation and colonization of Palestinian territories, discrimination against Palestinian citizens of Israel, and the denial of the right of return for Palestinian refugees. Drawing inspiration from the successful South African anti-apartheid movement, BDS encourages collective action to pressure Israel to adhere to international law.
Since its inception in 2005, the BDS movement has become a dynamic, worldwide endeavor, encompassing unions, academic associations, churches, and grassroots organizations. It has made a substantial impact in challenging international support for Israeli apartheid and settler-colonialism.

Ongoing Injustice
For nearly seven decades, Israel has denied Palestinians their basic rights and has consistently flouted international law. This prolonged injustice persists due to unwavering international support. Governments have failed to hold Israel accountable for its actions, and corporations and institutions worldwide have played a role in perpetuating the oppression of Palestinians.
In response to the lack of action by those in power, Palestinian civil society has called for a global citizen response, rallying solidarity for the Palestinian cause and their struggle for freedom, justice, and equality.
Boycotts, Divestment, and Sanctions (BDS)
The BDS movement consists of three primary components:

- Boycotts: This involves withdrawing support from Israel’s apartheid regime, institutions involved in human rights violations, and international companies collaborating in such violations.
- Divestment: Divestment campaigns urge financial institutions, local councils, churches, pension funds, and universities to divest from the State of Israel and from Israeli and international entities that sustain Israeli apartheid.
- Sanctions: Sanctions campaigns pressure governments to fulfill their legal obligations to end Israeli apartheid, prevent any assistance in its maintenance, prohibit business with illegal Israeli settlements, halt military trade and free-trade agreements, and suspend Israel’s participation in international organizations, including UN bodies and FIFA.
The Call for BDS
The BDS movement was officially launched in 2005 when a coalition of 170 Palestinian civil society organizations called for the adoption of BDS as a non-violent means of pressuring Israel to comply with international law. The movement’s key demands include:
- Ending Occupation: Israel must cease its occupation and colonization of all Arab lands and dismantle the barrier separating Palestinian territories. International law recognizes the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, Gaza, and the Syrian Golan Heights as occupied by Israel. Israel’s actions, such as land appropriation and establishing illegal settlements, constitute a grave violation of this law. Gaza, under an Israeli blockade, has become one of the largest open-air prisons globally.
- Equality for Palestinian Citizens: The Arab-Palestinian citizens of Israel, who constitute one-fifth of its population, are entitled to full equality. Israel’s systematic racial discrimination against them, codified in over 50 laws, affects every aspect of their lives. This includes land dispossession and incitement to racial violence against them by Israeli leaders.
- Right of Return: Palestinian refugees, numbering over 7.25 million due to Israel’s forced displacement since 1948, have the right to return to their homes and properties as per UN Resolution 194. Israel’s denial of this right is based solely on the grounds of ethnicity.
It’s essential to underscore that BDS is an inclusive and anti-racist human rights movement that rejects all forms of discrimination, including anti-Semitism and Islamophobia.
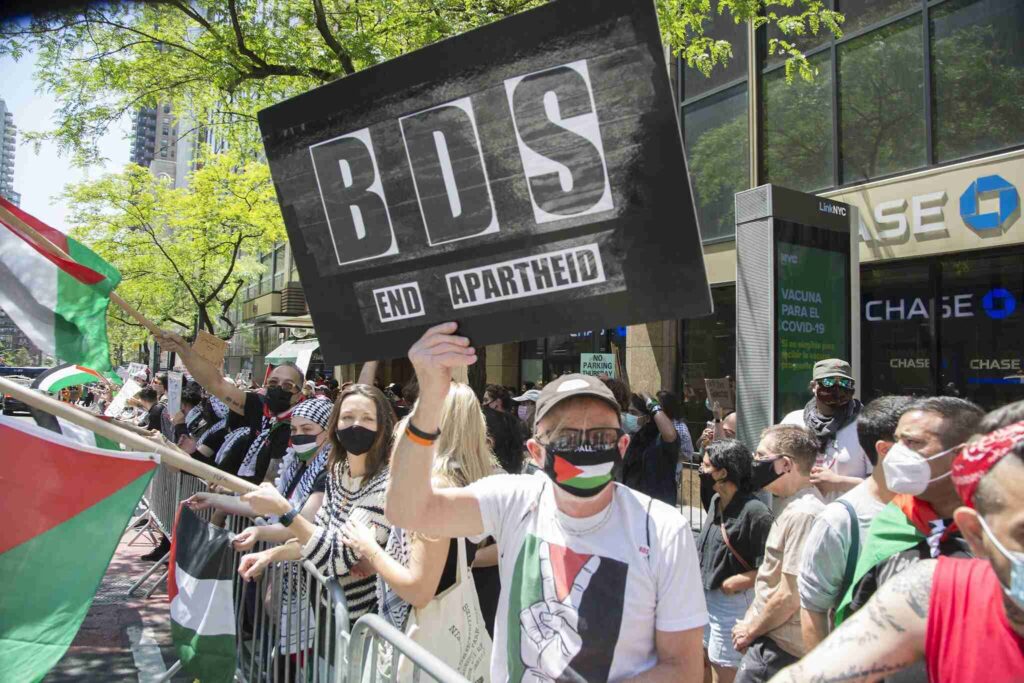

A Global Movement
The BDS movement enjoys substantial support from unions, churches, NGOs, and diverse movements across every continent. Furthermore, there are vibrant BDS campaigns taking place in communities worldwide, and progressive Jewish groups play a significant role in the movement. Notable public figures, including Archbishop Desmond Tutu, Naomi Klein, Roger Waters, Angela Davis, and Judith Butler, have endorsed BDS.
Growing Impact
BDS has been gaining substantial traction thanks to strategic campaigning. Its impact includes:
- BDS Campaigns in the Arab World: BDS campaigns are intensifying in the Arab world, with companies like G4S losing numerous contracts and investments in various countries.
- Economic Impact: BDS has contributed to a 46% drop in foreign direct investment in Israel, and Israeli exporters are facing challenges in trading with Europe.
- Veolia’s Withdrawal: French multinational Veolia withdrew from Israel due to a BDS campaign, leading to substantial financial losses.
- G4S’s Announcement: G4S, a security services company, planned to sell its Israeli subsidiary after BDS pressure.
- Cultural Boycott: Thousands of artists and cultural figures, such as Roger Waters and Lauryn Hill, support the cultural boycott of Israel.
- Academic Support: Academic associations in several countries have voted to support BDS, and various student unions have done the same.
- Church Divestments: US churches and several Quaker bodies have voted to divest from Israeli and international companies targeted by BDS.
- Government and Bank Divestments: Government pension funds in various countries and renowned investors have divested from BDS-targeted companies.
- Israel’s Perception: Israel considers BDS a “strategic threat” to its ongoing oppression of Palestinians and allocates significant resources to counter BDS efforts.
- Corporate Responses: Companies like Orange and SodaStream faced boycotts and divestments due to their associations with Israeli policies.
- Academic Boycott: Renowned scientist Stephen Hawking boycotted an Israeli conference, and universities have severed ties with Israeli institutions.
- Local Council Support: Over 50 councils in Spain and many more in other countries have passed motions supporting BDS initiatives.
- EU Regulations: The EU has implemented regulations that prohibit funding for Israeli companies based in illegal settlements, raising awareness about the illegality of such businesses.
- Port Actions: Community actions have prevented Israeli ships from docking at ports in various countries, including the US, South Africa, Sweden, and India.
- Loss of Contracts: Israeli state water company Mekorot has lost contracts in several countries due to its involvement in Israel’s apartheid water policies.
- Government Blacklisting: The Kuwaiti government blacklisted 50 companies due to BDS campaigning.
- Government Actions: Governments have taken action, such as suspending free trade agreement talks with Israel during the 2014 attacks on Gaza.
See also: List of Artists Supporting Israel Zionists

BDS activist, Please express your support for the Palestinian cause by using this wallpaper collection.
The BDS movement aims to end international support for Israeli violations of international law, forcing entities and governments to change their policies. As Israeli entities become isolated, Israel will face increasing challenges in its oppression of Palestinians. BDS campaigns also raise global awareness of Israel’s treatment of the Palestinian population.
The growth and success of the BDS movement send a resounding message that people around the world are unwilling to accept Israel’s continued oppression of Palestinians.